The µLight technology
The µLight sources are composed of pixels, like those of a telephone screen.
Each pixel can be controlled in intensity and color using software developed by leida Technologies: it is thus possible to form particular patterns to illuminate the samples observed in transmission.
µLight 59 pixels source
The 59 pixels source which equips the standard models of the sources µLight.

Pattern for bright field
The numerical aperture can be adjusted by selecting the number of rings lit.

Pattern for Zernike phase contrast
With a phase contrast lens, you can switch from brightfield to phase with a simple click of the computer mouse.

Pattern for Rheinberg
In conventional microscopy, Rheinberg illumination is achieved by placing filters in the condenser. With µLight, a simple click is enough.
Pattern for oblique illumination
The oblique illumination allows to visualize in real time transparent objects, with eyepieces or with a camera.

Logo µLight
A little smile.
Example 1: Visual Focus Assist
In order to make the focus with a microscope, we have designed a two-wave illumination method that allows to split the image of an object when it is not in focus.
When in focus, the two images are superimposed.
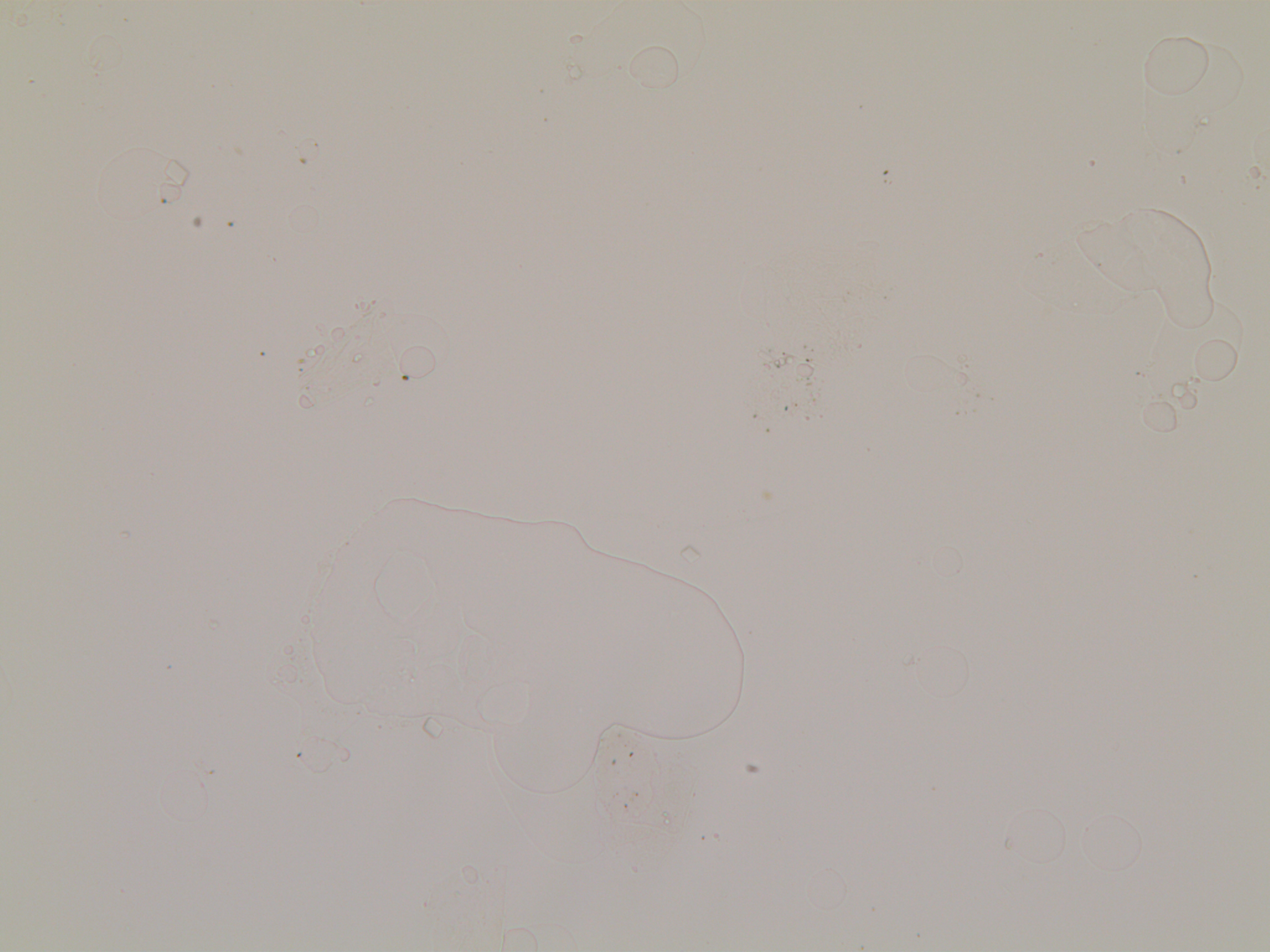
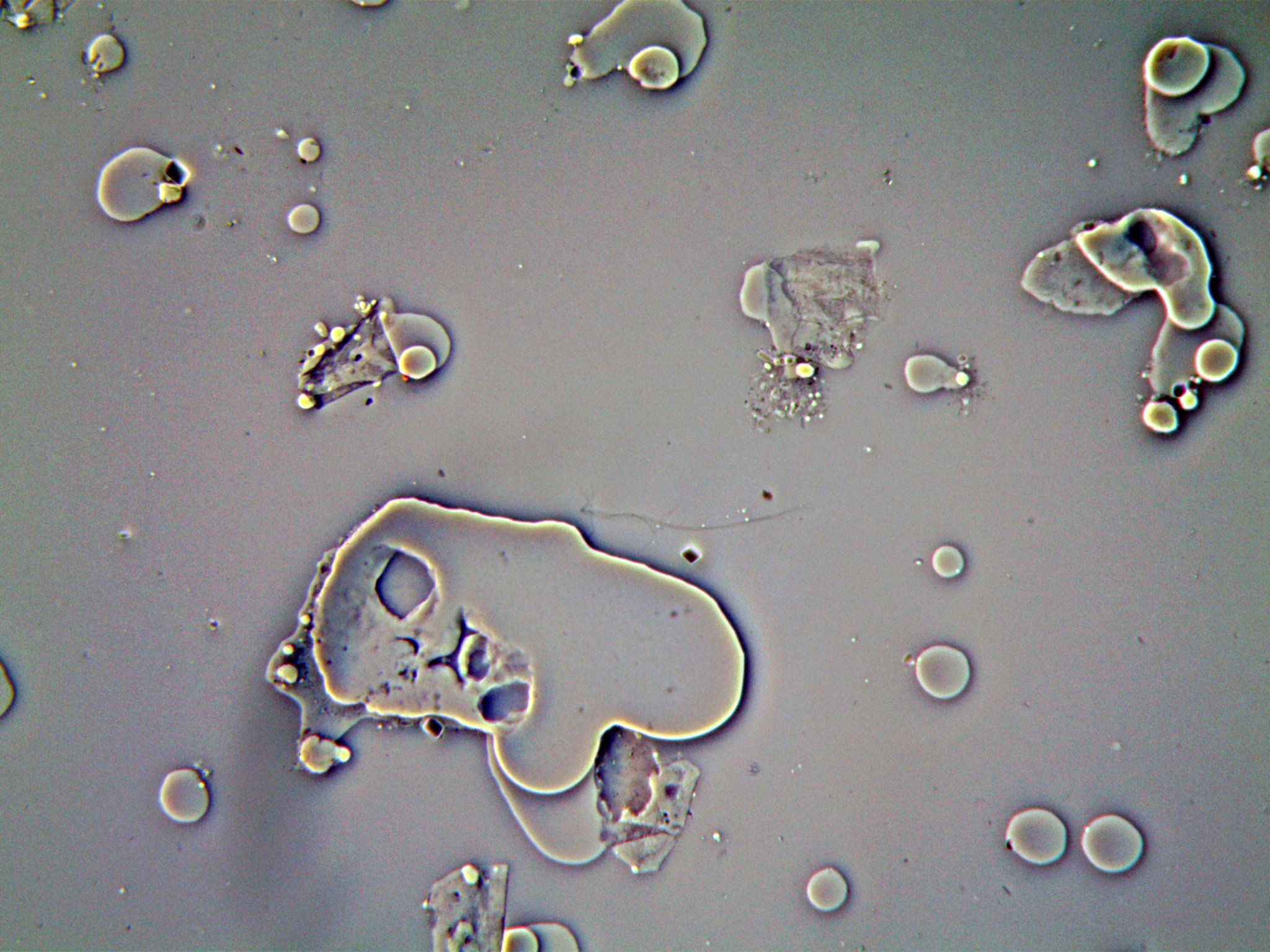
Illustration below: on the left, the blurred images, on the right, the focus is assured.
First line: images in VFA. Second line: the same images in bright field.
The method is simple, fast and efficient.

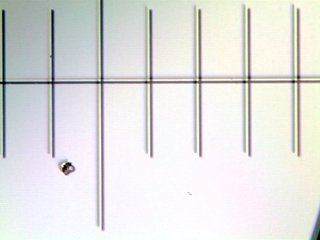
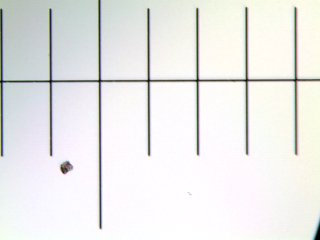
Images of a micrometer observed in VFA (patented by FR3076912).
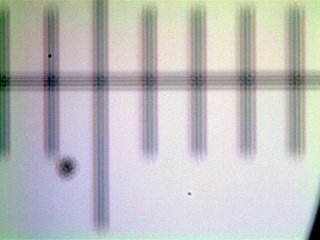
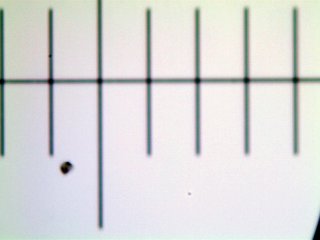
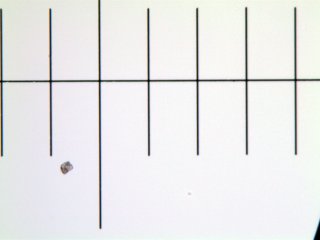
Images of a micrometer observed in bright field.
-
The depth of focus is greater in VFA than in bright field and it is easier to detect out-of-focus objects.
This method also allows to measure the focus defect to achieve an autofocus.
Example 2: Revealing the invisible
With a simple mouse click, it is possible to observe invisible structures against a light or dark background.
We have developed a new method of observation in phase contrast that is possible with standard lenses and light structuring (patent FR1770787).